In today’s digital era, the use of AI-driven image enhancement techniques in photography has revolutionized the way we capture and present moments. These technologies hold the promise of transforming ordinary snapshots into stunning masterpieces, but they also raise important ethical questions. Today we’ll explore the potential pitfalls of AI-driven enhancements, particularly concerning unrealistic beauty standards and the delicate balance between authenticity and artistic expression.
Enhancing Image Quality and Editing

AI-Driven Image Enhancement Techniques:
AI-powered tools have ushered in a new era of photo editing, where algorithms analyze and optimize images to improve various aspects such as exposure, colors, and sharpness. These advancements offer photographers and hobbyists unprecedented capabilities to enhance their work effortlessly. However, the ease of use and the potential to manipulate images can give rise to ethical concerns.
Unrealistic Beauty Standards:
One of the major ethical dilemmas stems from the reinforcement of unrealistic beauty standards through AI-driven photo retouching. In pursuit of the “perfect” image, AI algorithms may subtly alter facial features, body proportions, and skin textures, leading to unattainable ideals that can negatively impact body image perceptions and self-esteem.
Photographers and image editors must remain conscious of the consequences of heavily retouched images. Striving for authenticity and preserving natural characteristics can promote a healthier representation of beauty in photography.
Balancing Authenticity and Artistic Expression:
AI-driven enhancements can sometimes push the boundaries of reality, blurring the line between genuine moments and fabricated scenes. While artistic expression is valued in photography, it is essential to maintain transparency when images are substantially altered.
Photographers should consider the intent behind the use of AI tools. Is it to enhance the existing beauty of a scene or to manipulate it beyond recognition? Striving for a balance between artistic creativity and truthfulness can help foster a sense of trust between the viewer and the photographer.
Addressing Ethical Concerns:
To address the ethical concerns related to AI-driven image enhancements, consider the following practical tips:
- Be Mindful of the Intended Message: Reflect on the message your photos convey. Is it promoting unrealistic beauty standards or celebrating diversity and natural beauty?
- Educate and Empower: As a photographer or image editor, use your platform to raise awareness about the potential consequences of unrealistic retouching and the importance of authenticity in visual storytelling.
- Use AI as a Tool, not a Crutch: Embrace AI as a tool to enhance your creative vision, but don’t rely solely on it for the entire photographic process. Retain control over the final output to ensure ethical decision-making.
- Collaborate and Seek Feedback: Engage in discussions with models, clients, and viewers to understand their perspectives and ensure that your work resonates positively with the audience.
Automated Tagging and Metadata
AI-based tagging and metadata generation have emerged as game-changers, streamlining the process and enabling photographers to find and categorize images effortlessly. However, with this convenience comes significant privacy implications and the potential misuse of personal data. In this section, we’ll explore the benefits of AI-based tagging and metadata, while also delving into the importance of transparency and consent in safeguarding user privacy.
Benefits of AI-Based Tagging and Metadata Generation:

AI-driven automated tagging and metadata generation offers an array of advantages that enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of photo organization:
- Timesaving: Manually tagging images and entering metadata can be time-consuming. AI algorithms can swiftly analyze images, recognize objects, people, and scenes, and generate relevant tags and descriptions.
- Improved Searchability: By adding descriptive tags and metadata, photographers can easily search and retrieve specific images from vast collections, boosting productivity and creativity.
- Enhanced Discoverability: AI-generated metadata can aid viewers in discovering relevant images more easily, leading to a better overall user experience.
Privacy Implications and Potential Misuse of Personal Data:
While AI-based tagging can be beneficial, it raises concerns about privacy and data protection:
- Identifiable Information: Automated tagging may inadvertently reveal sensitive information about individuals present in the images, such as their location, preferences, or affiliations.
- Data Security: Storing vast amounts of personal data in the form of tags and metadata requires robust security measures to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Algorithmic Bias: AI algorithms can unintentionally perpetuate biases in tagging, leading to misrepresentations or underrepresentation of certain groups or demographics.
Ensuring Transparency and Consent:
To address privacy concerns related to AI-based tagging and metadata generation, it is crucial to adopt transparent practices and prioritize user consent:
- Clear Privacy Policies: Photography platforms and AI developers must have transparent privacy policies that outline how data will be used, shared, and stored.
- Anonymization Techniques: Employ anonymization techniques to protect the identities of individuals in images and ensure that personal data is not readily accessible.
- Opt-In Consent: Request explicit user consent for utilizing AI-generated tags and metadata, allowing individuals to have control over their data.
- Regular Audits: Periodic audits and assessments of AI algorithms should be conducted to identify and rectify any biases that might arise during the tagging process.
Facial Recognition and Privacy
Role of Facial Recognition in Photography:
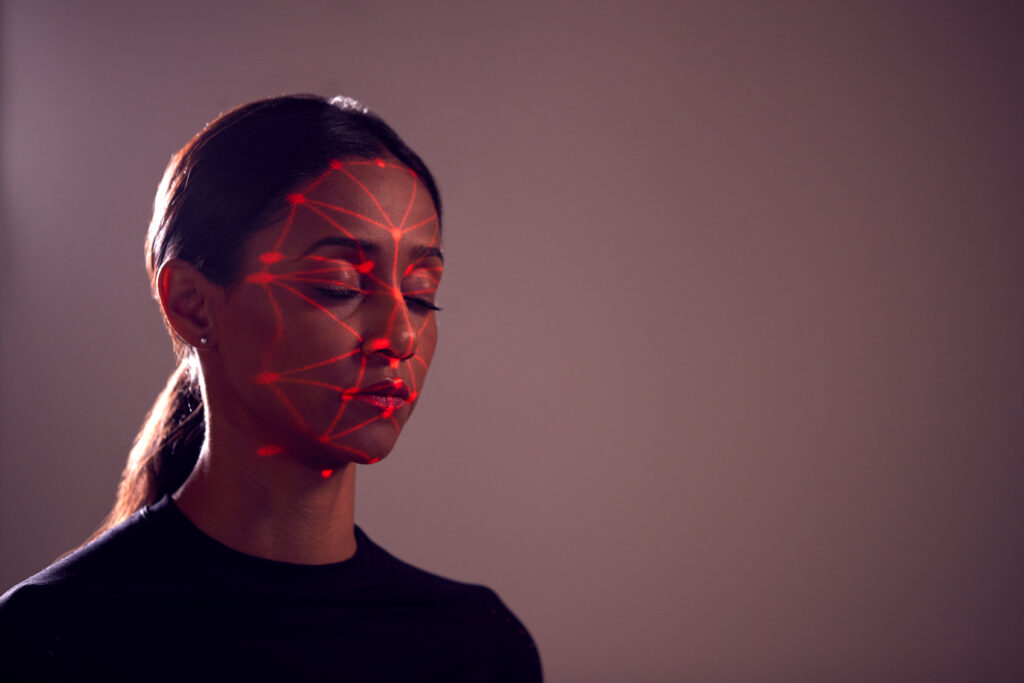

Facial recognition has revolutionized how we interact with photographs, allowing us to quickly identify and tag individuals in images. From automatic tagging on social media platforms to sorting photos based on recognized faces, technology has streamlined the organization and retrieval of visual memories.
Additionally, facial recognition in photography plays a crucial role in areas like biometric authentication, forensic investigations, and even creative applications, such as generating animated emojis based on facial expressions.
Privacy Concerns and Potential for Misuse:
While facial recognition offers undeniable convenience, it comes with serious privacy considerations:
- Informed Consent: Using facial recognition to identify and tag individuals without their knowledge or explicit consent raises ethical questions about the ownership and control of personal data.
- Surveillance and Tracking: Widespread deployment of facial recognition in public spaces raises concerns about constant surveillance and the potential abuse of this technology for tracking and monitoring individuals without their knowledge.
- Biases and Misidentifications: Facial recognition algorithms can exhibit biases, leading to misidentifications, particularly for certain demographics, which can have severe consequences, such as wrongful arrests or discrimination.
The misuse of facial recognition technology in photography has sparked real-life controversies and legal challenges:
- Clearview AI Scandal: The case of Clearview AI, a controversial facial recognition company, demonstrated how AI-powered algorithms scrapped billions of images from social media platforms, raising concerns about the lack of consent and data protection.
- Racial Bias in Recognition: Several studies have shown that certain facial recognition systems exhibit racial bias, leading to misidentifications and disparities in accuracy based on race.
Guidelines for Responsible Use and Safeguarding Individual Privacy:
To ensure the ethical and responsible use of facial recognition in photography, consider the following guidelines:
- Prioritize Consent: Obtain explicit consent from individuals before using their facial data for recognition purposes, respecting their right to privacy.
- Implement Strong Security Measures: Employ robust security protocols to safeguard facial data and prevent unauthorized access or breaches.
- Address Bias and Accuracy: Regularly assess facial recognition algorithms for biases and work towards improving accuracy across diverse demographics.
- Limit Surveillance Use: Exercise restraint in deploying facial recognition for mass surveillance purposes, respecting individuals’ right to anonymity in public spaces.
Bias and Representation
AI-driven photography tools have the potential to revolutionize the way we capture and interpret the world around us. However, these tools are only as good as the data they are trained on. When AI models are fed biased datasets, it can lead to skewed results and perpetuate the underrepresentation or misrepresentation of certain groups.
Impact of Bias in Training Datasets on AI-Driven Photography Tools:
Training datasets are a crucial component of AI algorithms, serving as the foundation on which the models learn to recognize patterns and make predictions. If these datasets contain biases, such as underrepresentation of certain demographics or overrepresentation of others, AI-driven photography tools may produce inaccurate or unfair results.
For instance, if a facial recognition algorithm is primarily trained on images of one racial group, it may struggle to accurately identify individuals from other racial backgrounds, leading to misidentifications and perpetuating harmful stereotypes.
Addressing Issues of Underrepresentation and Misrepresentation:
To tackle the issue of bias in AI-driven photography tools, several steps can be taken:
- Diverse and Representative Datasets: AI developers should ensure that training datasets are diverse and representative of the population they aim to serve. This includes images from different regions, cultures, and demographics to avoid skewed results.
- Ongoing Evaluation and Improvement: Continuously monitor the AI algorithms for biases and inaccuracies, making improvements based on feedback and real-world performance to reduce misrepresentations.
- Engaging with Marginalized Communities: Collaborate with individuals from underrepresented groups to better understand their needs and perspectives, ensuring that AI tools cater to diverse audiences.
Promoting Diversity and Inclusivity in AI-Based Photography:
Encouraging diversity and inclusivity in AI-based photography is not just about eliminating biases but also about proactively promoting equitable representation:
- Inclusive Image Libraries: Companies like Getty Images have taken steps to increase diversity in their collections by offering images that portray people from various backgrounds, abilities, and gender identities.
- Crowd-Sourced Datasets: Encourage the collection of diverse images through crowd-sourced platforms, where photographers from different communities can contribute to building more inclusive datasets.
- Ethical Guidelines: Establish and adhere to ethical guidelines that promote fairness and inclusivity in AI-driven photography, setting a standard for the industry.
In 2018, a study by MIT researchers found that popular facial recognition systems showed higher error rates for women and individuals with darker skin tones compared to men and those with lighter skin tones. This highlights the real-world consequences of biased training datasets on AI technologies.
Getty Images, a leading stock photo agency, has taken steps to address representation issues by creating the “Inclusion Collection.” This collection features photos that challenge stereotypes and offer a more diverse portrayal of individuals from various backgrounds.
Copyright and Intellectual Property

The rise of AI technology has introduced exciting possibilities in photography, with AI-generated or assisted photographs becoming increasingly common. However, these advancements also give rise to complex issues concerning copyright ownership, proper attribution, and the legal and ethical implications of AI-generated derivative works.
AI-Generated or Assisted Photographs and Copyright Ownership:
Copyright ownership in AI-generated or assisted photographs can be a tricky area to navigate. Traditionally, the copyright for a photograph belongs to the person who took the photo—the photographer. However, when AI is involved in the creative process, the lines can blur.
For instance, if an AI system generates a photograph with minimal human input, determining the sole creator and copyright owner becomes challenging. In such cases, legal experts must consider the degree of human input, the level of AI’s autonomy, and any agreements between the AI developer and photographer to determine copyright ownership.
Ensuring Proper Attribution and Copyright Compliance:
Regardless of the involvement of AI in the creative process, proper attribution and copyright compliance are essential ethical practices:
- Transparency in Attribution: When using AI tools to enhance or generate photographs, photographers should be transparent about the involvement of AI and give appropriate credit for the technology’s contribution.
- Licensing and Usage Agreements: If photographers use third-party AI services, they should review licensing agreements carefully to understand copyright ownership and usage rights.
- Creative Commons and Public Domain: When sharing AI-generated photographs, adhering to Creative Commons licenses and public domain guidelines ensures proper usage and attribution.
Legal and Ethical Implications of AI-Generated Derivative Works:
AI-generated derivative works—photos that are modified or built upon using AI—are a novel area with significant legal and ethical implications:
- Fair Use Considerations: Using AI to create transformative derivative works may raise fair use arguments, but it’s essential to consider the impact on the original creator’s rights.
- Respect for Creative Intent: AI developers and photographers should exercise ethical judgment when using AI to alter or remix copyrighted works, respecting the original creator’s creative intent.
- Potential Infringement: AI-generated derivative works that closely resemble copyrighted photographs might inadvertently infringe on the original creator’s copyright, leading to legal consequences.
In 2018, an AI-generated artwork titled “Portrait of Edmond de Belamy” was sold at auction for nearly half a million dollars. This raised questions about copyright ownership, as the AI system had no human creator in the traditional sense.
Additionally, companies like Adobe have introduced AI-powered features that allow users to seamlessly alter and manipulate photographs. Such tools present new challenges for copyright compliance and attribution.
Proper attribution, compliance with licensing agreements, and thoughtful consideration of AI-generated derivative works are essential for fostering a fair and sustainable ecosystem in AI-driven photography. Let’s navigate this new frontier responsibly, ensuring that AI enhances creativity while preserving the rights and integrity of creators.
Manipulation and Authenticity

The Line Between Artistic Manipulation and Deceptive Practices:
Artistic manipulation in photography has a rich history, dating back to the days of darkroom editing. With AI technology, the possibilities for creative alterations have expanded significantly. However, a critical distinction must be made between enhancing artistic expression and engaging in deceptive practices that mislead viewers.
While artistic manipulation allows photographers to evoke emotions, highlight subjects, and create captivating visuals, crossing the line into deceptive practices involves altering images to portray false narratives or misrepresent reality. This can erode trust and undermine the credibility of visual storytelling.
Disclosure and Transparency in AI-Generated or Altered Images:
To maintain trust and integrity in AI-driven photography, photographers should prioritize disclosure and transparency:
- Clear Statements: When sharing AI-generated or significantly altered images, photographers should accompany them with clear statements about the use of AI and the extent of manipulation. This enables viewers to understand the creative process and make informed interpretations.
- Ethical Intent: Photographers should consider the ethical intent behind the manipulation. Is it enhancing the visual narrative, or is it misleading viewers by altering essential elements of the scene?
- Contextual Information: Providing context around AI-assisted edits can help viewers differentiate between artistic expression and deceptive practices.
Preserving Trust and the Integrity of Visual Storytelling:

The trust between photographers and their audience is paramount in visual storytelling. To preserve this trust and uphold the integrity of the medium, consider the following:
- Empathy and Empowerment: Be mindful of the emotional impact of your images on viewers and aim to empower them with truth and authenticity.
- Responsible Editing: Use AI technology responsibly, understanding that creative expression should not compromise the core truth of a photograph.
- Journalistic Integrity: For photojournalists, adhering to ethical standards is crucial in preserving the credibility and integrity of the stories they capture.
Accountability and Regulation
As AI-driven photography continues to shape the creative landscape, the need for ethical guidelines and industry standards becomes ever more crucial. Accountability and regulation are essential to ensure that AI technologies in photography are used responsibly and ethically.
Need for Ethical Guidelines and Industry Standards:
With AI’s expanding influence in photography, it is imperative to establish clear ethical guidelines and industry standards. Such policies may address issues like the following:
- Consent and Privacy: Ensuring that individuals’ consent is obtained before using their data for AI applications and safeguarding their privacy throughout the process.
- Bias Mitigation: Implementing measures to identify and correct biases in AI algorithms to avoid perpetuating stereotypes and discriminations.
- Authenticity and Disclosure: Encouraging transparency in AI-generated or altered images and disclosing the use of AI technology to maintain the authenticity of visual storytelling.
Roles of Photographers, Developers, and Policymakers:
All stakeholders play crucial roles in fostering ethical AI-driven photography:
- Photographers: As creators and users of AI tools, photographers should prioritize transparency, respect for privacy, and ethical considerations in their work. They can also advocate for responsible AI practices within their community.
- Developers: AI developers have the responsibility to build ethical algorithms, identify and address biases, and design AI systems that prioritize user privacy and consent.
- Policymakers: Governments and regulatory bodies must collaborate with industry experts to establish legal frameworks and guidelines for AI in photography, ensuring that technology advances responsibly and ethically.
The Importance of Ongoing Dialogue and Collaboration:
Creating ethical standards and navigating the complexities of AI-driven photography requires ongoing dialogue and collaboration among stakeholders:
- Multidisciplinary Engagement: Engage professionals from various fields, such as photography, AI development, ethics, and law, to develop comprehensive and well-balanced guidelines.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Establish feedback mechanisms to collect insights from photographers, developers, and the public, to continuously improve and adapt ethical guidelines.
In the ever-evolving world of AI and machine learning in photography, ethical considerations are paramount. As we explored the various aspects of this transformative technology, from enhancing image quality to facial recognition and AI-generated photography, it becomes clear that responsible practices are essential. By being mindful of biases, promoting diversity, and prioritizing transparency and consent, we can harness the power of AI while preserving the authenticity and integrity of visual storytelling. As photographers, developers, policymakers, and consumers, let us embrace a future where AI in photography is guided by ethical principles, inspiring creativity, and fostering trust with each captivating image we create and share.






